Applications and advantages of vacuum drying technology
1. Basic Principles of Vacuum Drying
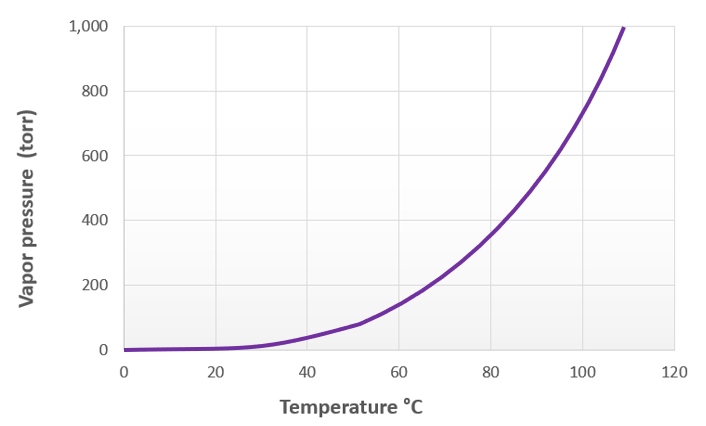
Vacuum drying is an advanced drying technology widely used in industry and laboratories. It utilizes a vacuum pump to reduce the pressure in an enclosed space, causing the solvent to boil and evaporate at a lower temperature. Lowering the pressure decreases the boiling point of the solvent. For example, as shown in the right figure, the boiling point of water at normal temperature and pressure is 100°C. As the pressure decreases, the boiling point of water also decreases. Therefore, by reducing the pressure using a vacuum, water can rapidly evaporate under low-temperature conditions.
2. Applications of Vacuum Drying
(1) Pharmaceutical Industry:
In the pharmaceutical industry, vacuum drying is widely used to dry heat-sensitive drugs, active ingredients, and antibiotics. Because vacuum drying can be carried out at low temperatures, it effectively protects the activity and stability of the drugs, preventing the destruction of the drug structure caused by high temperatures. Additionally, vacuum drying prevents drugs from decomposing or deteriorating at high temperatures, ensuring product quality.
(2) Food Industry:
In the food industry, vacuum drying is mainly used to dry fruits, vegetables, meat, and seafood. By lowering the drying temperature, vacuum drying maximizes the retention of nutrients, color, and flavor in the food. For example, vacuum freeze-drying (lyophilization) is a common vacuum drying method that dehydrates food at low temperatures, preserving its original form and nutritional value.
(3) Chemical Industry:
In the chemical industry, vacuum drying is primarily used for drying polymers, catalysts, and intermediate chemicals. These materials often have heat sensitivity or are prone to oxidation. Vacuum drying effectively avoids these issues, improving product purity and stability.
(4) Biotechnology:
In the biotechnology field, vacuum drying is commonly used to dry enzymes, proteins, and other bioactive substances. These substances are temperature-sensitive, and vacuum drying can be conducted at low temperatures to ensure their activity and functionality are not compromised.
3. Advantages of Vacuum Drying
(1) Protecting Material Quality:
Vacuum drying can be performed at low temperatures, avoiding the destruction of heat-sensitive substances and maintaining the chemical structure and physical properties of the materials. This is particularly important for high-value materials such as pharmaceuticals, food, and biological products.
(2) Improving Drying Efficiency:
Since vacuum drying significantly lowers the boiling point of the solvent, the drying process is accelerated, enhancing production efficiency. This is especially beneficial for industries requiring large-scale production, such as pharmaceuticals and food processing.
(3) Energy Saving:
Vacuum drying operates at lower temperatures, requiring less thermal energy, which helps save energy and reduce production costs. This is an important consideration in modern industry, contributing to increased competitiveness and sustainable development.
4. Conclusion
With its advantages of low temperature, high efficiency, energy saving, and environmental protection, vacuum drying has become an indispensable drying technology in modern industry. Whether in pharmaceuticals, food, chemicals, or biotechnology, vacuum drying demonstrates excellent performance and extensive application prospects. As technology continues to advance, vacuum drying technology will keep evolving, providing higher quality and more efficient drying solutions for various industries. It is hoped that this in-depth discussion will offer valuable reference and guidance to professionals in related fields, further enhancing the application level of vacuum drying technology.
References

Vacuum drying is an advanced drying technology widely used in industry and laboratories. It utilizes a vacuum pump to reduce the pressure in an enclosed space, causing the solvent to boil and evaporate at a lower temperature. Lowering the pressure decreases the boiling point of the solvent. For example, as shown in the right figure, the boiling point of water at normal temperature and pressure is 100°C. As the pressure decreases, the boiling point of water also decreases. Therefore, by reducing the pressure using a vacuum, water can rapidly evaporate under low-temperature conditions.
2. Applications of Vacuum Drying
(1) Pharmaceutical Industry:
In the pharmaceutical industry, vacuum drying is widely used to dry heat-sensitive drugs, active ingredients, and antibiotics. Because vacuum drying can be carried out at low temperatures, it effectively protects the activity and stability of the drugs, preventing the destruction of the drug structure caused by high temperatures. Additionally, vacuum drying prevents drugs from decomposing or deteriorating at high temperatures, ensuring product quality.
(2) Food Industry:
In the food industry, vacuum drying is mainly used to dry fruits, vegetables, meat, and seafood. By lowering the drying temperature, vacuum drying maximizes the retention of nutrients, color, and flavor in the food. For example, vacuum freeze-drying (lyophilization) is a common vacuum drying method that dehydrates food at low temperatures, preserving its original form and nutritional value.
(3) Chemical Industry:
In the chemical industry, vacuum drying is primarily used for drying polymers, catalysts, and intermediate chemicals. These materials often have heat sensitivity or are prone to oxidation. Vacuum drying effectively avoids these issues, improving product purity and stability.
(4) Biotechnology:
In the biotechnology field, vacuum drying is commonly used to dry enzymes, proteins, and other bioactive substances. These substances are temperature-sensitive, and vacuum drying can be conducted at low temperatures to ensure their activity and functionality are not compromised.
3. Advantages of Vacuum Drying
(1) Protecting Material Quality:
Vacuum drying can be performed at low temperatures, avoiding the destruction of heat-sensitive substances and maintaining the chemical structure and physical properties of the materials. This is particularly important for high-value materials such as pharmaceuticals, food, and biological products.
(2) Improving Drying Efficiency:
Since vacuum drying significantly lowers the boiling point of the solvent, the drying process is accelerated, enhancing production efficiency. This is especially beneficial for industries requiring large-scale production, such as pharmaceuticals and food processing.
(3) Energy Saving:
Vacuum drying operates at lower temperatures, requiring less thermal energy, which helps save energy and reduce production costs. This is an important consideration in modern industry, contributing to increased competitiveness and sustainable development.
4. Conclusion
With its advantages of low temperature, high efficiency, energy saving, and environmental protection, vacuum drying has become an indispensable drying technology in modern industry. Whether in pharmaceuticals, food, chemicals, or biotechnology, vacuum drying demonstrates excellent performance and extensive application prospects. As technology continues to advance, vacuum drying technology will keep evolving, providing higher quality and more efficient drying solutions for various industries. It is hoped that this in-depth discussion will offer valuable reference and guidance to professionals in related fields, further enhancing the application level of vacuum drying technology.
References
Image source: [https://www.pearson.com/channels/general-chemistry](https://www.pearson.com/channels/general-chemistry)

